Fiber optic technology has revolutionized modern communication by enabling ultra-fast data transmission with minimal loss. As organizations expand their networks, one of the most common questions is: What’s the difference between Single Mode and Multi Mode fiber optic cables?
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into both fiber types, their advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications so you can make an informed decision for your business or project.
Table of Contents
?What is Fiber Optic Cable
A fiber optic cable uses strands of glass or plastic to transmit data in the form of light. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables provide:
Higher bandwidth capacity
Faster data speeds
Greater reliability over long distances
Immunity to electromagnetic interference
There are two main categories of fiber optic cables: Single Mode Fiber (SMF) and Multi Mode Fiber (MMF). Each serves different purposes depending on distance, cost, and bandwidth requirements.
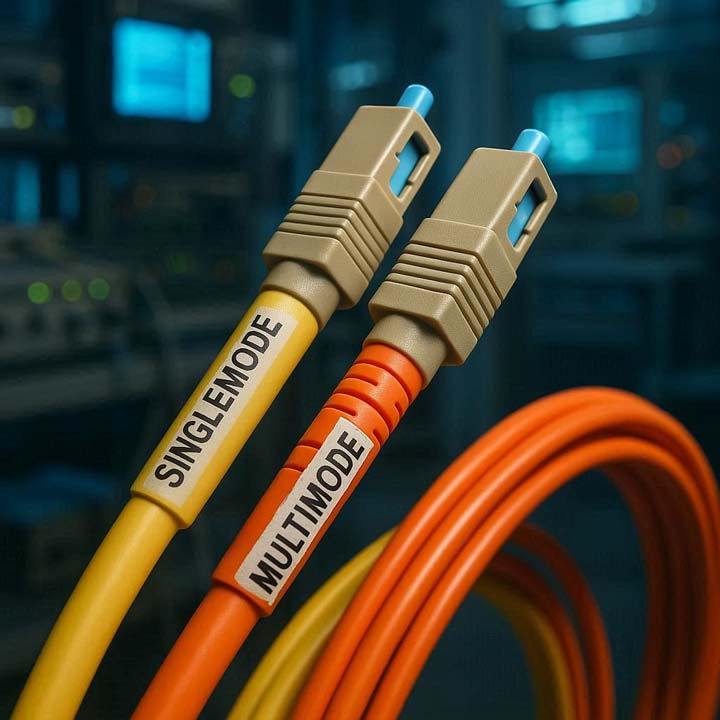

?What is Single Mode Fiber (SMF)
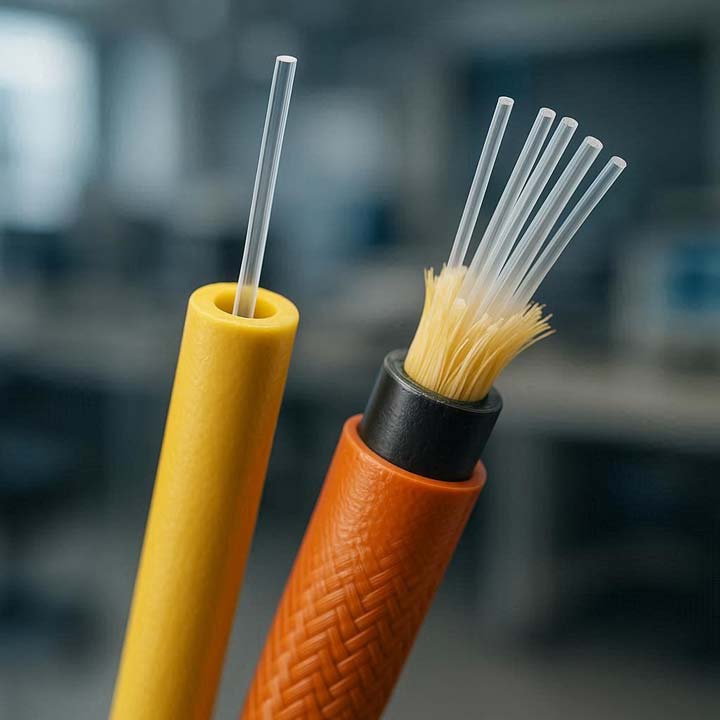
Single Mode Fiber is designed with a very small core size (approximately 8–10 microns). This narrow core allows light to travel in a single path, reducing reflection and signal dispersion.
:Features of Single Mode Fiber
Transmission Distance: Can carry data over tens of kilometers without significant signal loss.
Bandwidth: Offers extremely high bandwidth, supporting 100 Gbps and beyond.
Light Source: Uses laser-based transmitters for precision and performance.
Applications: Ideal for telecommunication backbones, metro networks, long-distance data transmission, and large-scale enterprises.
Read More: What is a Fiber Optic Patch Cord?
:Advantages of Single Mode Fiber
Supports the highest data rates.
Future-proof for growing bandwidth demands.
Best option for long-distance communication.
:Disadvantages of Single Mode Fiber
Higher cost compared to Multi Mode.
Requires more expensive transceivers and installation equipment.

?What is Multi Mode Fiber (MMF)
Multi Mode Fiber features a larger core size (50–62.5 microns), which allows multiple light modes to travel simultaneously. This increases modal dispersion but simplifies installation.
:Features of Multi Mode Fiber
Transmission Distance: Typically up to 500–600 meters depending on cable type (OM2, OM3, OM4, OM5).
Bandwidth: Sufficient for most short-distance networking applications.
Light Source: Works with LEDs or VCSELs, which are cost-effective.
Applications: Commonly used in local area networks (LANs), data centers, and enterprise building connections.
:Advantages of Multi Mode Fiber
More affordable than Single Mode.
Easy to install and terminate.
Perfect for short-distance communication.
:Disadvantages of Multi Mode Fiber
Limited range compared to SMF.
Lower bandwidth potential for future high-speed demands.
?Which Fiber is Right for You
When choosing between Single Mode and Multi Mode fiber, consider:
Distance: If you need to connect buildings across a city, Single Mode is the best option. For data center connections under 600m, Multi Mode is sufficient.
Budget: Multi Mode is more cost-effective, while Single Mode is an investment in future-proofing.
Bandwidth Needs: For cutting-edge speeds and scalability, Single Mode wins.
Future Trends in Fiber Optics
With the rise of 5G networks, cloud computing, and IoT, the demand for higher bandwidth and lower latency continues to grow. Many organizations are moving towards Single Mode Fiber for its scalability, but Multi Mode Fiber still dominates in enterprise-level LANs and short-distance applications.

Final Thoughts
Both Single Mode and Multi Mode fiber optic cables play crucial roles in today’s networking infrastructure. The right choice depends on your distance requirements, budget, and long-term goals.
At ParsAndishanProshat, we provide professional consultation and installation services for both Single Mode and Multi Mode fiber networks. Whether you need a high-capacity backbone or a reliable local network, our experts will help you design the perfect solution.




بدون دیدگاه